Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Toyoda, Satoshi*; Yoshimura, Masashi*; Sumida, Hirosuke*; Mineoi, Susumu*; Machida, Masatake*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Suzuki, Satoru*; Yokoyama, Kazushi*
Hoshako, 35(3), p.200 - 206, 2022/05
The present status of spatiotemporal depth profiling analysis of the multilayer stacked film interface based on Ambient Pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (APXPS) is presented. To begin with, depth profiles of the multilayer stacked film interfaces have been achieved by time-division Near Ambient Pressure Hard X-ray Angle-Resolved PhotoEmission Spectroscopy data. We then have promoted our methods to quickly perform peak fittings and depth profiling from time-division angle resolved AP-XPS data including spatial resolution, which enables us to realize spatiotemporal depth profiles of the interfaces under reaction conditions such as oxidation and reduction. In addition, it is found that the traditional maximum entropy method (MEM) combined with Jackknife averaging of sparse modeling is effective to perform dynamic measurement of depth profiles with high precision.
 Si with XPS and XAS
Si with XPS and XASEsaka, Fumitaka; Nojima, Takehiro; Udono, Haruhiko*; Magara, Masaaki; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki
Surface and Interface Analysis, 48(7), p.432 - 435, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:39.42(Chemistry, Physical)XPS is widely used for non-destructive chemical state analysis of solid materials. In this method, depth profiling can be carried out by a combination with ion beam sputtering. However, the sputtering often causes segregation and preferential sputtering of atoms and gives inaccurate information. The use of energy-tunable X-rays from synchrotron radiation (SR) enables us to perform non-destructive depth profiling in XPS. Here, the analytical depth can be changed by changing excitation X-ray energy. In the present study, we examined methods to perform depth profiling with XPS by changing excitation energy and XAS by changing electron energy for detection. These methods were then applied to the analysis of native surface oxide layers on Mg Si crystals. In this XAS analysis, the peak at 1843.4 eV becomes dominant when the electron energy for detection increases, which implies that Si-O or Si-O-Mg structure is formed as the surface oxide layer on the Mg
Si crystals. In this XAS analysis, the peak at 1843.4 eV becomes dominant when the electron energy for detection increases, which implies that Si-O or Si-O-Mg structure is formed as the surface oxide layer on the Mg Si.
Si.
Kobata, Masaaki; Kobayashi, Keisuke*
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 58(2), p.43 - 49, 2015/02
We report the applications of a hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy to the characterization of SiO /Si(001)systems. Large escape depth of high-energy photoelectron enables us to probe buried layers and their interfaces in multilayer structures. Estimation of SiO
/Si(001)systems. Large escape depth of high-energy photoelectron enables us to probe buried layers and their interfaces in multilayer structures. Estimation of SiO overlayer thicknesses up to 25 nm by angle resolved XPS was possible in SiO
overlayer thicknesses up to 25 nm by angle resolved XPS was possible in SiO /Si(001) samples. Determination of the thickness profile of a wedged shape SiO
/Si(001) samples. Determination of the thickness profile of a wedged shape SiO buried layer was successfully done in Ir (8 nm)/HfO
buried layer was successfully done in Ir (8 nm)/HfO (2.2 nm)/thickness graded-SiO
(2.2 nm)/thickness graded-SiO (0-10 nm) / Si (100). The Si 1s core level showed a SiO
(0-10 nm) / Si (100). The Si 1s core level showed a SiO thickness dependent shift, which was ascribed to fixed charge at the SiO
thickness dependent shift, which was ascribed to fixed charge at the SiO -Si interface. Energy distribution of interface states at ultrathin thermal oxide/Si(100) interfaces were determined by Si 1
-Si interface. Energy distribution of interface states at ultrathin thermal oxide/Si(100) interfaces were determined by Si 1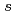 core level shift by applying gate bias in metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structure with 5 nm Au gate electrodes.
core level shift by applying gate bias in metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structure with 5 nm Au gate electrodes.
 -FeSi
-FeSi thin films on Si(III) surface by solid phase epitaxy (SPE) analyzed by means of synchrotron radiation XPS (SR-XPS)
thin films on Si(III) surface by solid phase epitaxy (SPE) analyzed by means of synchrotron radiation XPS (SR-XPS)Saito, Takeru; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Asaoka, Hidehito; Haraguchi, Masaharu*; Imamura, Motoyasu*; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Tanaka, Tomoaki*; Shimada, Hiromichi*; Hojo, Kiichi
Analytical Sciences (CD-ROM), 17(Suppl.), p.1073 - 1076, 2002/03
no abstracts in English
 -FeSi
-FeSi on Si(111) substrate studied by means of SR-XPS
on Si(111) substrate studied by means of SR-XPSSaito, Takeru; Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Haraguchi, Masaharu*; Imamura, Motoyasu*; Matsubayashi, Nobuyuki*; Tanaka, Tomoaki*; Shimada, Hiromichi*; Hojo, Kiichi
Photon Factory Activity Report 2001, (19), P. 205, 2001/00
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Baba, Yuji
Journal of the Korean Vacuum Society, 9(S2), p.84 - 88, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
 /Si layer by high-energy XPS
/Si layer by high-energy XPSYamamoto, Hiroyuki; Baba, Yuji
Journal of Surface Analysis, 7(1), p.122 - 127, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
 /Si layer
/Si layerYamamoto, Hiroyuki; Baba, Yuji
Photon Factory Activity Report 1998, P. 136, 1999/11
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Hiroyuki; Baba, Yuji; Sasaki, Teikichi
Photon Factory Activity Report, (13), P. 352, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
*; Kawanishi, Shunichi; Nishii, Masanobu; Shimizu, Yuichi; Sugimoto, Shunichi; *; *
J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol., 6(3), p.385 - 392, 1993/00
no abstracts in English
 Si pn-junction diode
Si pn-junction diodeHori, Nobuhiko*; Esaka, Fumitaka; Udono, Haruhiko*
no journal, ,
Magnesium half silicide is a semiconductor with an indirect energy gap of about 0.6 eV at room temperature. This material is attracting attention as a suitable material for Si-based infrared photo detector. In this study, Ag diffusion coefficient was evaluated for the Ag diffused Mg Si substrate using a conventional sputter etching. In addition, the sensitivity of the diode was improved by controlling the Ag diffusion depth. As the result, the sensitivity of the diode with the diffusion depth of 20
Si substrate using a conventional sputter etching. In addition, the sensitivity of the diode was improved by controlling the Ag diffusion depth. As the result, the sensitivity of the diode with the diffusion depth of 20  m was four times higher than that with the diffusion depth of 80
m was four times higher than that with the diffusion depth of 80  m.
m.
 solid by depth analysis with photo-electron spectroscopy
solid by depth analysis with photo-electron spectroscopySekiguchi, Tetsuhiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yano, Masahiro; Asaoka, Hidehito; Suzuki, Shinichi*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
In the recovery process for the laser isotope separation of cesium Cs-135, we need occlusion material that takes the photo-generated atomic Cs selectively, but does not take CsI molecules. In the present study, fullerene C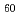 was selected as an occlusion material. Concentration depth distribution of Cs in the solid was evaluated using X-ray photo-electron spectroscopy (XPS). The dependence of the X-ray excitation energy for Cs
was selected as an occlusion material. Concentration depth distribution of Cs in the solid was evaluated using X-ray photo-electron spectroscopy (XPS). The dependence of the X-ray excitation energy for Cs or CsI
or CsI dosed C
dosed C samples were measured. Difference in excitation energy dependence were observed between Cs and CsI. In Cs, the results were explained by the distribution that penetrated deeply into the solid. On the other hand, it was concluded that CsI did not penetrate into the solid.
samples were measured. Difference in excitation energy dependence were observed between Cs and CsI. In Cs, the results were explained by the distribution that penetrated deeply into the solid. On the other hand, it was concluded that CsI did not penetrate into the solid.